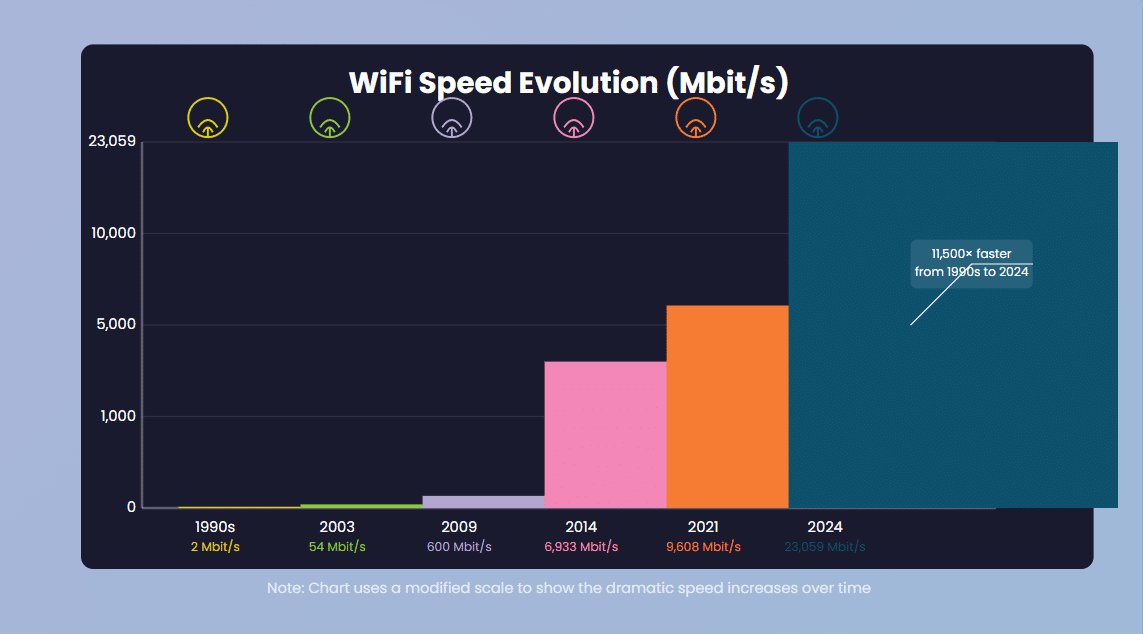
The Evolution of WiFi
Posted on 17 June 2025 by Beaming SupportDo you want to know how WiFi has changed? In this post we journey through the evolution of WiFi, from its humble beginnings in the 1990s to the lightning-fast connections we can enjoy today!
💡1990s: The Birth of WiFi (IEEE 802.11)
- What happened?
The first WiFi protocol (IEEE 802.11) was introduced, inspired by research from teams in Holland and the United States. - Speed: Up to 2 Mbit/s
- Fun Fact: At the time, most UK internet users were still on 56Kbps dial-up connections!
🛒1999: WiFi Goes Commercial
- What happened?
Apple launched the iBook laptop with built-in WiFi and the AirPort Wireless base station, making wireless internet accessible to consumers. - Impact: Wireless internet became mainstream, despite limited speed and range compared to today, but considering that the average broadband connection in the UK at the time was 56Kbps with a dial up connection, it was amazing.
⬆2003: Enter IEEE 802.11g
- What happened?
The 802.11g standard was ratified, pushing WiFi speeds to new heights. - Speed: Up to 54 Mbit/s
- Range: Still using the 2.4GHz band for good coverage.
📶2009: WiFi 4 (IEEE 802.11n) Changes the Game
- What happened?
Introduction of dual-band WiFi, adding the 5GHz spectrum alongside 2.4GHz. - Speed: Up to 600 Mbit/s
Trade-off: 5GHz offered faster speeds but shorter range, 2.4GHz provided longer range but lower speeds. The new update was more affected by walls and windows, but the fact it ran both signals simultaneously meant that users would experience the higher speeds when closer to the router or access point but would still be able to connect at further away but with slower speeds.
⚡2014: WiFi 5 (IEEE 802.11ac) Arrives
- What happened?
WiFi 5 focused on the 5GHz spectrum, delivering a massive speed boost. - Speed: Up to 6,933 Mbit/s
- Note: 2.4GHz devices remained on the older WiFi 4 standard, which some saw as a drawback as a lot of users still relied on the 2.4Ghz spectrum for longer range connections.
🌐2021: WiFi 6 & WiFi 6E (IEEE 802.11ax) – The Next Leap
- What happened?
WiFi 6 brought higher speeds and reintroduced 2.4GHz for better compatibility. WiFi 6E added the new 6GHz band. - Speed: Up to 9,608 Mbit/s
- Benefit: 6GHz spectrum offered faster speeds at longer ranges, bridging the gap between 2.4GHz and 5GHz.
👑2024: WiFi 7 (IEEE 802.11be) – The Ultimate Standard
- What happened?
WiFi 7 unified all three spectrums (2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz) under one protocol. - Speed: Up to 23,059 Mbit/s
- Impact: The fastest, most versatile WiFi yet!
➡Interested in the history of the internet? Read about the changes over the past 20 years in this Beaming report